Dallas
214-456-2333
Fax: 214-456-2714
Plano
469-303-4300
Fax: 469-303-4310
Park Cities
469-488-7000
Fax: 469-488-7001
Prosper
469-303-5000
Fax: 214-867-9511
Request an Appointment with codes: Cardiology (Heart Center)
Children's Health℠ is one of only 30 centers nationwide certified as a Center of Excellence by the Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Association, underscoring our ability to provide specialized, expert care for your child. Our team works hand-in-hand with heart specialists, genetic experts, dieticians and other field leaders to provide careful monitoring and treatment for children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
214-456-2333
Fax: 214-456-2714
469-303-4300
Fax: 469-303-4310
469-488-7000
Fax: 469-488-7001
469-303-5000
Fax: 214-867-9511
Request an Appointment with codes: Cardiology (Heart Center)
Pediatric HCM causes all or part of the heart muscle to become thicker than usual (hypertrophic). The thicker heart muscle often has difficulty relaxing, which can make it harder to pump blood. This in turn can lead to irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmia), and in some cases, heart failure.
While most children with HCM lead long lives, it is a serious condition that can cause heart failure or sudden cardiac death. Because of this, children with HCM should be followed regularly by a Children’s Health cardiologist with expertise in caring for individuals with this condition.
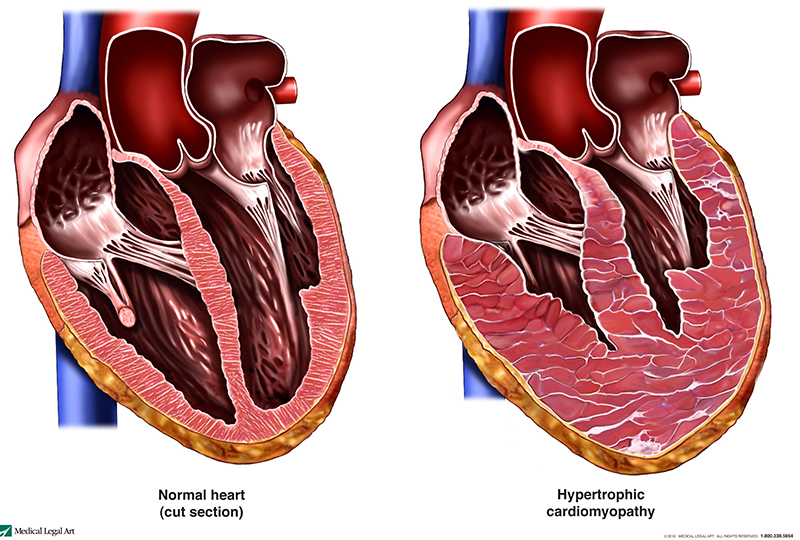
Pediatric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a complex condition that can start at any time in a child’s life, which can make diagnosis challenging. This is why it’s important to work with experts who know what to look for.
At Children’s Health, we use several different tests to help detect hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in infants, children and teenagers. The most common test we use to diagnose HCM is a heart ultrasound (echocardiogram), which uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. This helps our team see if the heart muscle is thicker than it should be, and can show whether the heart’s chambers are working as usual.
Other tests we may use to diagnose HCM include:
Pediatric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy has many causes. The condition can be passed to children from their parents through genes (inherited) or it can be caused by spontaneous gene changes. Other times, there is no clear cause (idiopathic).
In some cases, HCM is caused by genetic mutations that affect only the heart muscle. In other cases, HCM is a result of another gene-related condition. Common types of genetic conditions that can cause HCM include:
While there is currently no cure for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, experts at Children’s Health can help ease your child’s symptoms and manage complications and challenges as they arise.
Children with HCM should be restricted from competitive sports or high-intensity exercise, which increase the risk of a sudden cardiac arrest. However, regular physical activity is still very important and we will help you find what level and types of physical activity are best for your child.
We help you inform your child’s school and coaches about HCM. For example, we can provide a letter informing the school that your child should not be graded on exercise performance (which could unintentionally pressure your child to push past their limits).
Sometimes medications can help manage symptoms or treat HCM. The most common medications are beta blockers, which slow down the heart rate and give the heart more time to fill with blood in between heartbeats.
Our team may offer an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) if your child is at high risk of sudden cardiac death. An ICD will monitor your child’s heart rhythm and can deliver an electrical signal to normalize the heart rhythm if needed.
Uncommonly, if medication isn’t relieving your child’s symptoms, we may discuss surgery to remove some of the abnormal heart muscle (surgical myectomy). In rare cases, we may need to discuss heart transplantation.
Many children with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy will never have symptoms and are at low risk of having sudden cardiac arrest. However, because HCM is a serious condition that can lead to more health problems over time, it’s essential to work with an expert team to monitor and manage your child’s health.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy can result in significant health complications, including heart failure and cardiac arrest. Our team may suggest lifestyle changes, medication or surgical treatment options to reduce the chances of these complications.
With proper screening and treatment, most people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy will live as long as the general population.